deadlock avoidance
![]()
![]()
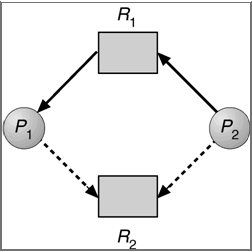 Resource-Allocation Graph For Deadlock Avoidance
Resource-Allocation Graph For Deadlock Avoidance
![]()
![]()
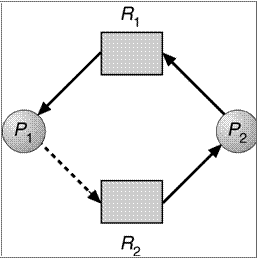 Unsafe State In Resource-Allocation Graph
Unsafe State In Resource-Allocation Graph
Banker’s Algorithm
- Multiple instances.
- Each process must a priori claim maximum use.
- When a process requests a resource it may have to wait.
- When a process gets all its resources it must return them in a finite amount of time.
Data Structures for the Banker’s Algorithm
 Let n = number of processes, and m = number of resources types.
Let n = number of processes, and m = number of resources types.
- Available: Vector of length m. If available [j] = k , there are
k instances of resource type Rj available.
- Max: n x m matrix. If Max [i,j] = k, then process Pi may request at most k instances of resource type Rj.
- Allocation: n x m matrix. If Allocation[ i,j] = k then Pi is currently allocated k instances of Rj.
- Need: n x m matrix. If Need[i,j] = k , then Pi may need k
more instances of Rj to complete its task. Need [i,j] = Max[i,j] – Allocation [i,j].