Annulenes
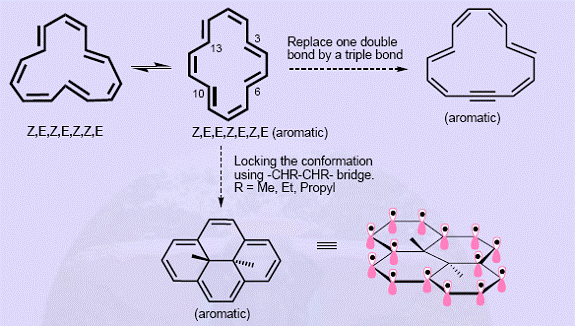
[14]-annulene Bond lengths in [14]-annulene range from 1.35-1.41Ao but do not show the alternating pattern of localized polyenes.It is aromatic (except for the isomers that are not planar). NMR shows that it is in conformational equilibrium as shown below (Figure 11). The steric interactions associated with internal hydrogens can be minimized if C3, C6, C10 and C13 positions are locked using suitable bridging units. Thus trans-15,16-dimethyldihydropyrene and its diethyl and dipropyl homologs are aromatic with C-C bond distances between 1.39-1.40 Ao. Conformational flexibility in [14]-annulene can be restricted by inserting triple bond in place of one of the more double bonds. Here, the triple bond contributes only two electrons for delocalization leaving the other two localized.
[16]-annulene [16]-annulene shows significant bond alteration, characteristic of a polyene structure (C-C, 1.46Ao; C=C, 1.34 Ao). It is nonplanar and is nonaromatic. Its dianion has been prepared and shows aromatic character (4n+2 system)
[18]-annulene
The cavity in [18]-annulene is sufficiently large and hence the steric interaction involving internal hydrogens is at minimum. The molecule is free of any significant angle strain, nearly planar, and show aromaticity. Its estimated resonance energy is 37 kcal/mol, which is in the range as that of benzene. The planarity and extent of delocalization in [18]-annulene can be improved by constructing its π periphery around a saturated core as in VIII . This compound shows significantly improved delocalization and aromaticity (2 times) compared to [18]-annulene.

