CASE STUDY-GSM PROTOCOL STACK
A GSM network is a bearer data communication protocol families. Any protocol stack for data communication, for example TCP/IP, can be implemented to use a bearer. GSM protocol architecture is - as for ISDN - structured into three independent planes
|
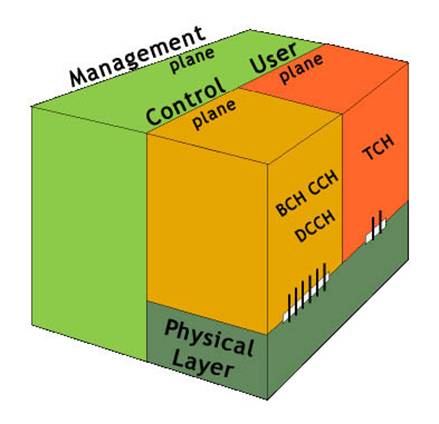
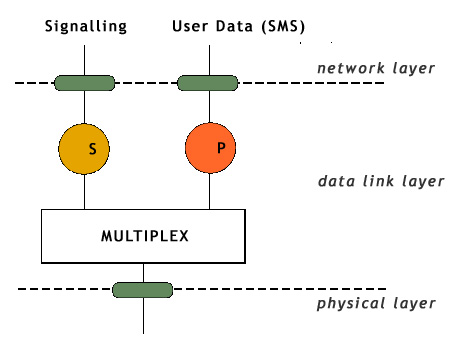
The user plane defines protocols to carry connection oriented voice and user data. At the radio interface Um, user plane data will be carried by the logical traffic channel called TCH. The control plane defines a set of protocols for controlling these connections with signalling information, for example signalling for connection setup. Such signalling data is carried over logical control channels called D-channels (Dm-channels). As the control channels often have spare capacities, also user data, the packet oriented SMS data, is transported over these channels.
Management plane function are plane management functions related to the system as a whole including plane coordinationfunctions related to resources and parameters residing in the layers of the control and/or user plane.Management of network element configuration and network element faults are examples of management plane functionality.